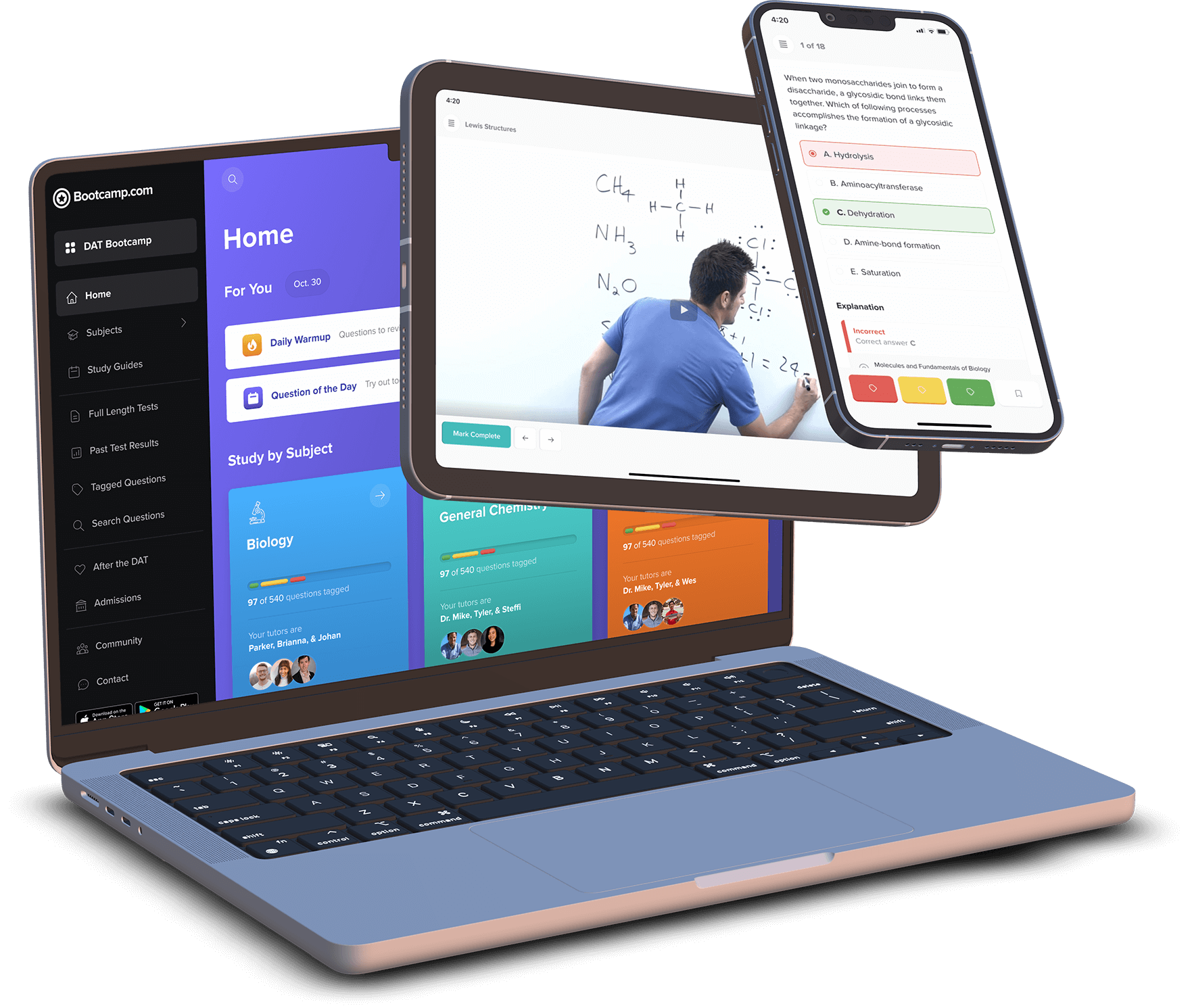
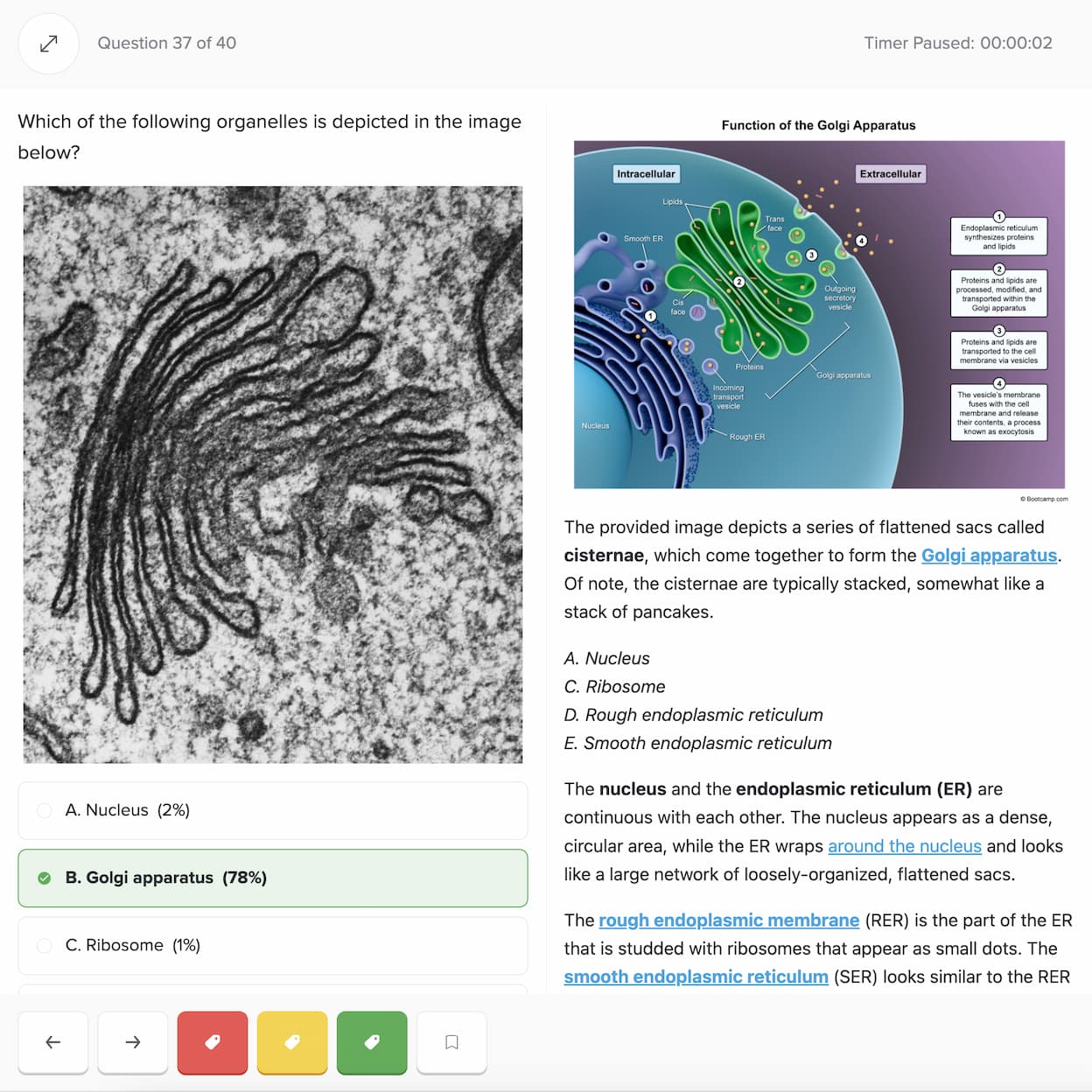
Practice with the most representative questions
 11,000+ high-yield DAT questions based on student feedback.
11,000+ high-yield DAT questions based on student feedback. Exam-like software interface and content.
Exam-like software interface and content. Weekly updates to maintain high standards of excellence.
Weekly updates to maintain high standards of excellence.
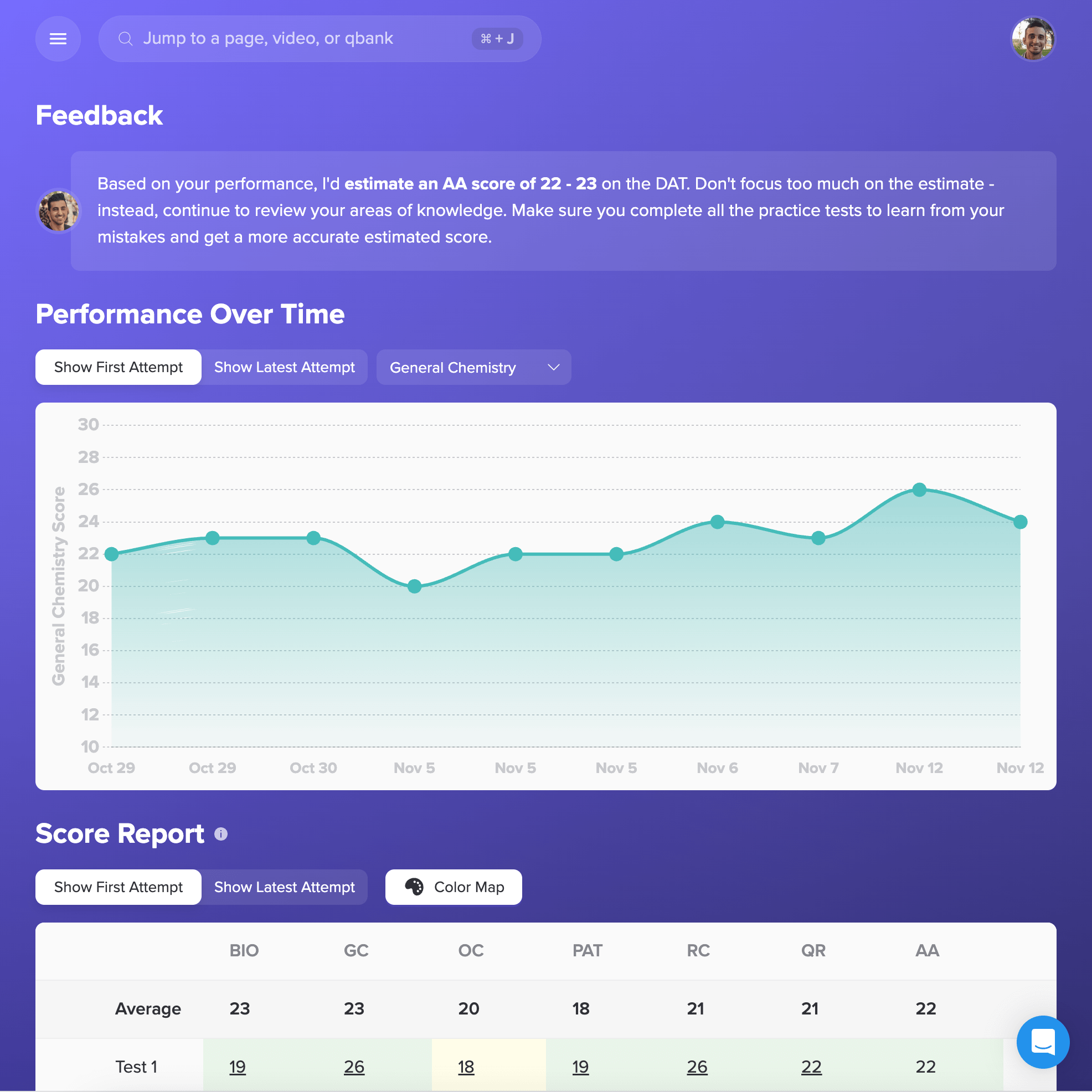
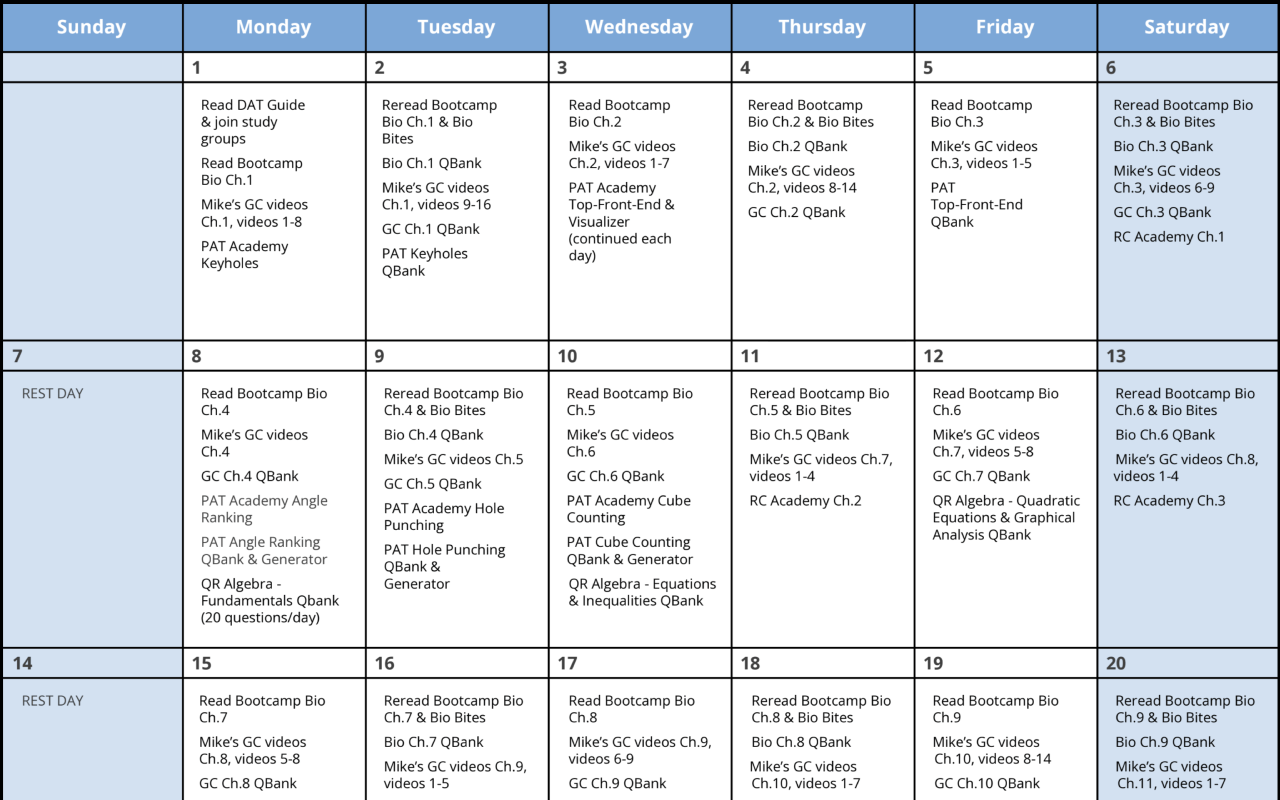
I want to emphasize that if you use Bootcamp EFFECTIVELY, you WILL be prepared for this exam. I made sure to do all ten of the Bootcamp practice exams, and these practice exams were VERY representative of the actual exam. If you are on a tight studying schedule like I was, definitely make it your priority to get through all of the practice exams, and focus on studying any concepts you struggled with that consistently showed up on practice exams.
















.jpg)



%20(1).jpg)


%20(1).jpg)
































